
Teaching English as a second language (ESL) is a rewarding yet complex endeavor that educators around the world engage in daily. While the global demand for English proficiency continues to rise, instructors face a myriad of challenges that can impact the effectiveness of language instruction. In this article, we will explore some of the key hurdles encountered by ESL teachers and discuss potential strategies to overcome them.
1. Diverse Student Backgrounds

One of the primary challenges in ESL classrooms is the diverse range of student backgrounds. Students may come from different linguistic, cultural, and educational backgrounds, making it challenging to tailor instruction to meet the needs of every individual. Addressing this challenge requires a flexible teaching approach that incorporates diverse learning styles and cultural sensitivity.
To overcome this challenge, ESL teachers can implement strategies such as using culturally relevant teaching materials, encouraging peer collaboration, and providing differentiated instruction based on students’ proficiency levels.
2. Limited English Proficiency Levels
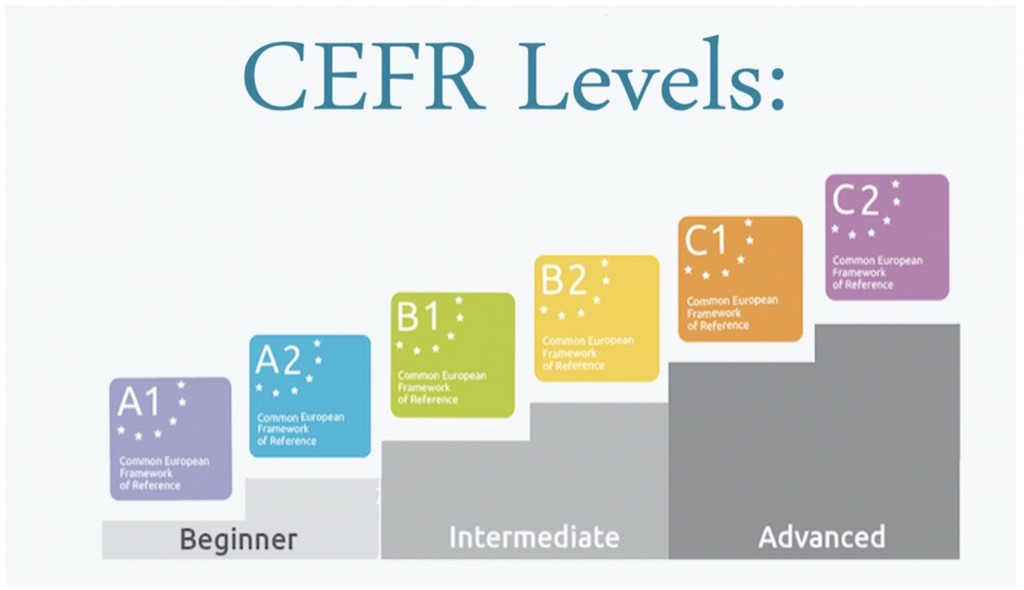
Teaching a class with students at varying English proficiency levels is a common scenario in ESL classrooms. Some students may have a basic understanding of English, while others may be more advanced. Striking a balance that challenges advanced learners without leaving beginners behind is a delicate task.
Instructors can address this challenge by incorporating activities that allow for differentiation, such as tiered assignments, small group work, and individualized assessments. Additionally, providing targeted feedback and setting realistic goals for each student can help foster a supportive learning environment.
3. Engaging Language Acquisition

Language acquisition is a complex process that goes beyond memorizing vocabulary and grammar rules. ESL teachers often face the challenge of keeping students engaged and motivated throughout the language-learning journey. Traditional methods that rely heavily on rote memorization may not be effective in the long term.
Incorporating interactive and communicative activities, such as role-playing, debates, and language games, can enhance engagement and make language acquisition a more enjoyable experience. Utilizing multimedia resources, including videos, podcasts, and interactive online platforms, can also create a dynamic learning environment.
4. Integrating Technology

While technology has the potential to enhance language learning, its integration into ESL classrooms is not without challenges. Limited access to technology, varying levels of digital literacy among students, and the need for reliable internet connectivity can hinder the effective use of technology in language instruction.
To address these challenges, ESL teachers can explore low-tech alternatives, such as incorporating audio resources, utilizing language learning apps that work offline, and integrating technology in a way that complements rather than replaces traditional teaching methods.
5. Assessment and Evaluation

Assessing language proficiency is a critical aspect of ESL instruction, but traditional assessment methods may not fully capture students’ linguistic abilities. Standardized tests may not account for the nuances of language use in real-life situations, and grading can be subjective.
Implementing a variety of assessment methods, including performance-based assessments, portfolios, and self-assessment, can provide a more comprehensive understanding of students’ language proficiency. Additionally, offering constructive feedback and involving students in the assessment process can contribute to their ongoing development.
6. Classroom Management in Multilingual Settings

In ESL classrooms, students may speak a variety of native languages, creating a multilingual environment. Managing diverse linguistic backgrounds while maintaining a cohesive learning atmosphere can be challenging for teachers.
Establishing clear communication norms, promoting a culture of respect and inclusion, and fostering a sense of community among students can contribute to effective classroom management in multilingual settings. Encouraging students to share their language and cultural experiences can create a rich and supportive learning environment.
Conclusion
Teaching English as a second language is a multifaceted undertaking that requires educators to navigate various challenges. From addressing diverse student backgrounds to incorporating technology and managing multilingual classrooms, ESL teachers play a crucial role in shaping the language proficiency of learners.
While these challenges may seem daunting, they also present opportunities for innovation and growth in the field of language education. By embracing flexibility, cultural sensitivity, and a student-centered approach, ESL teachers can create dynamic and inclusive learning environments that empower students to become proficient English speakers in an increasingly interconnected world.
